Muse
learning system
How do you think?
What do you think?
Learning how to think competent in all situations
MUSE learning is an education program unique to Kansai University Elementary School. For this program, about 12 lessons are allocated per year, in which children develop thinking skills by tackling tasks that require them to think competently in various situations. Through this system, students in the first to sixth grades systematically learn about how to approach the problems they face and how to use thinking tools to solve them.
Learning how to make full use of
six types of thinking tools
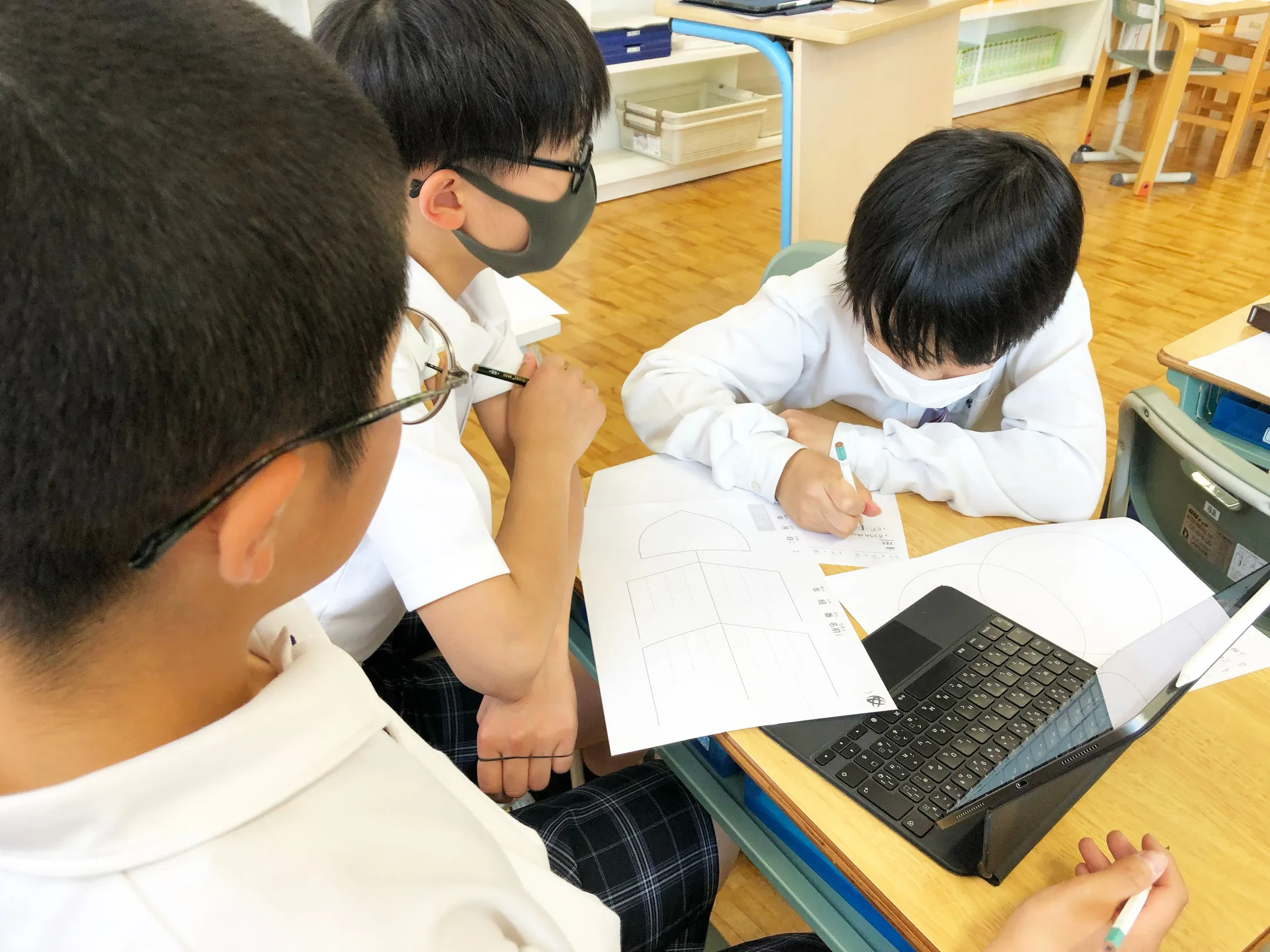
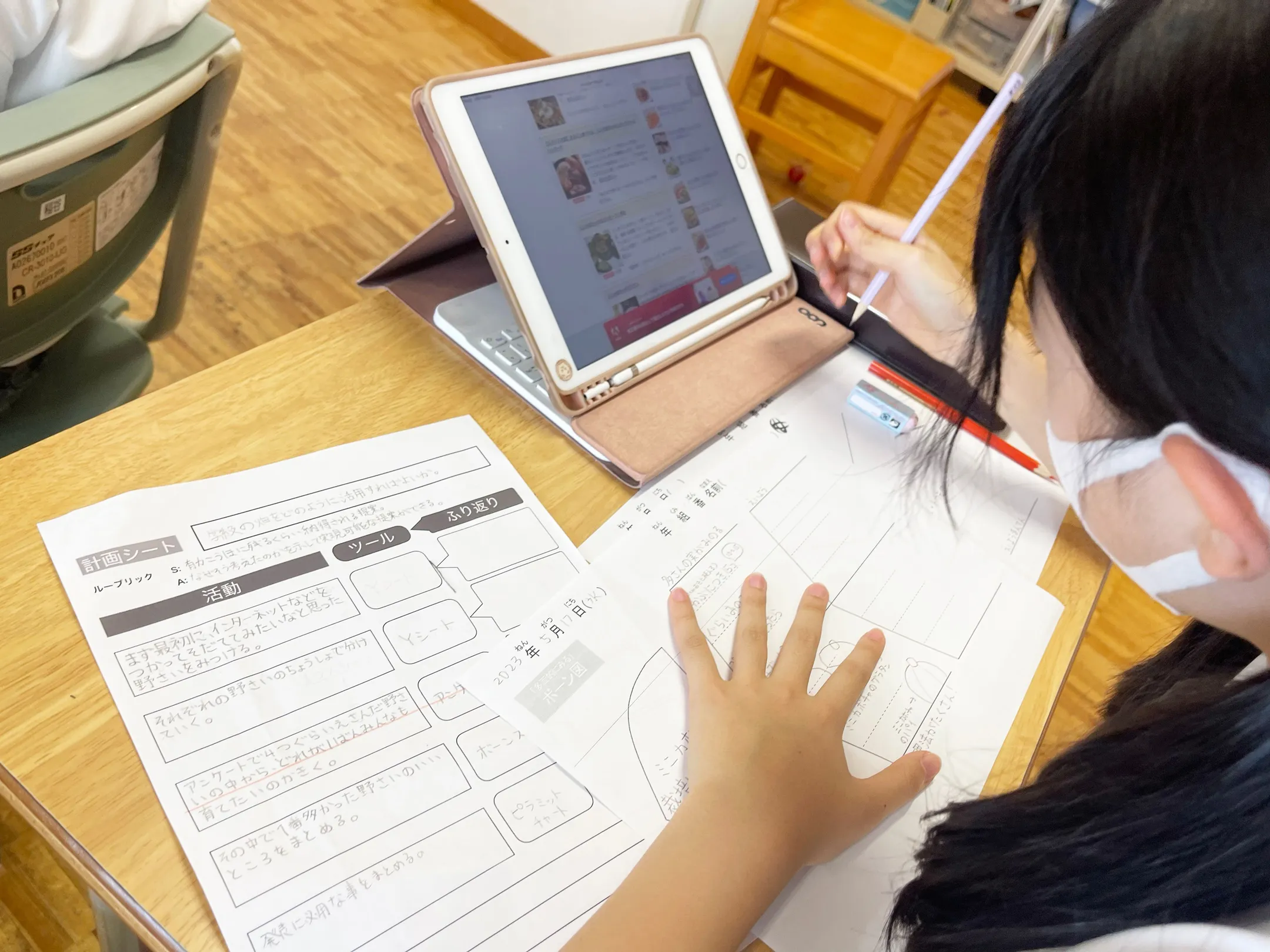
Young thinkers learn six major thinking skills (comparison, categorization, association, etc.) by using thinking tools. For example, students use thinking tools, such as a Venn diagram and an X-chart, to organize and visualize their ideas on a specific topic. They also share their written ideas with others in class, through which they learn thinking skills.
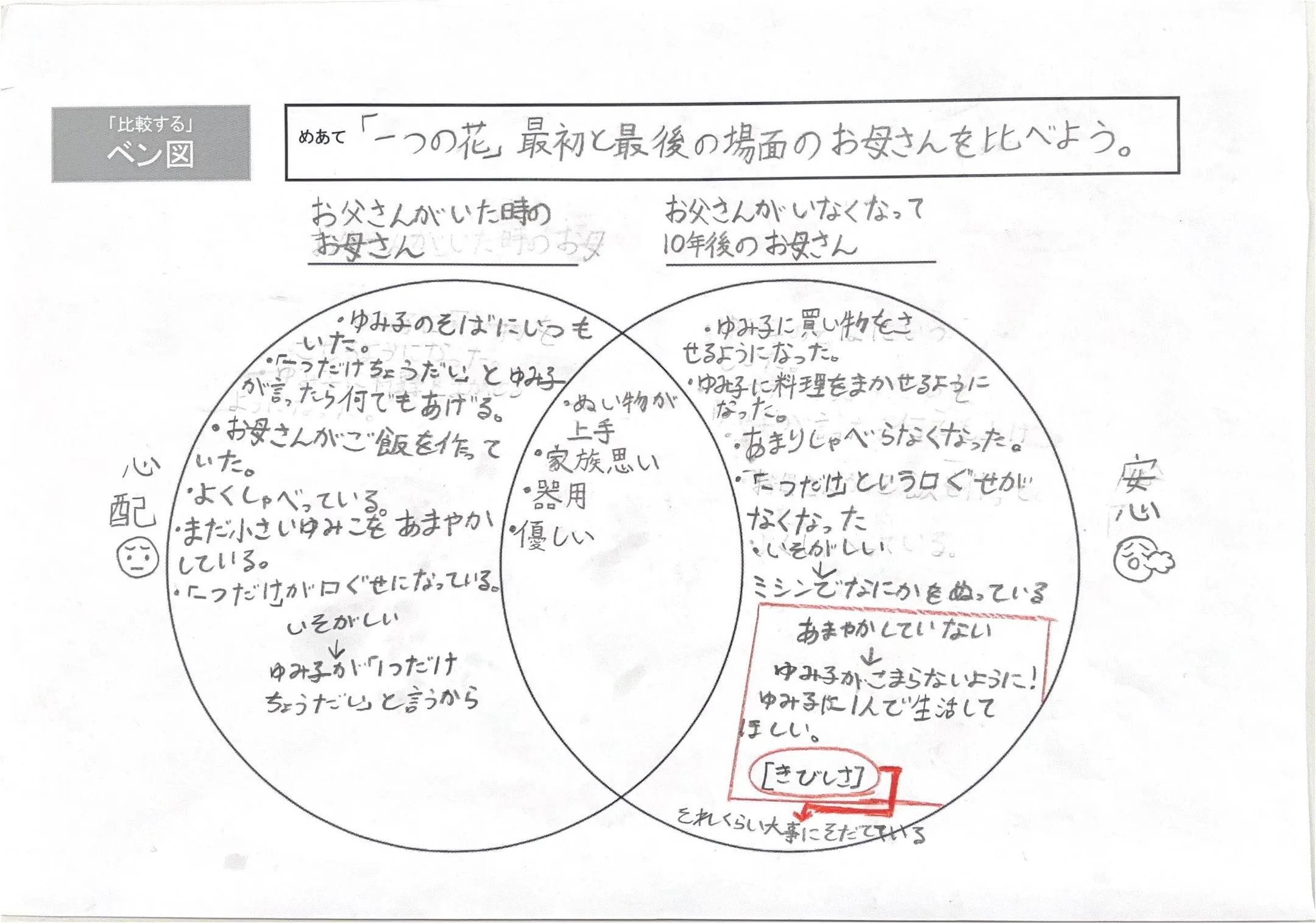
Comparison
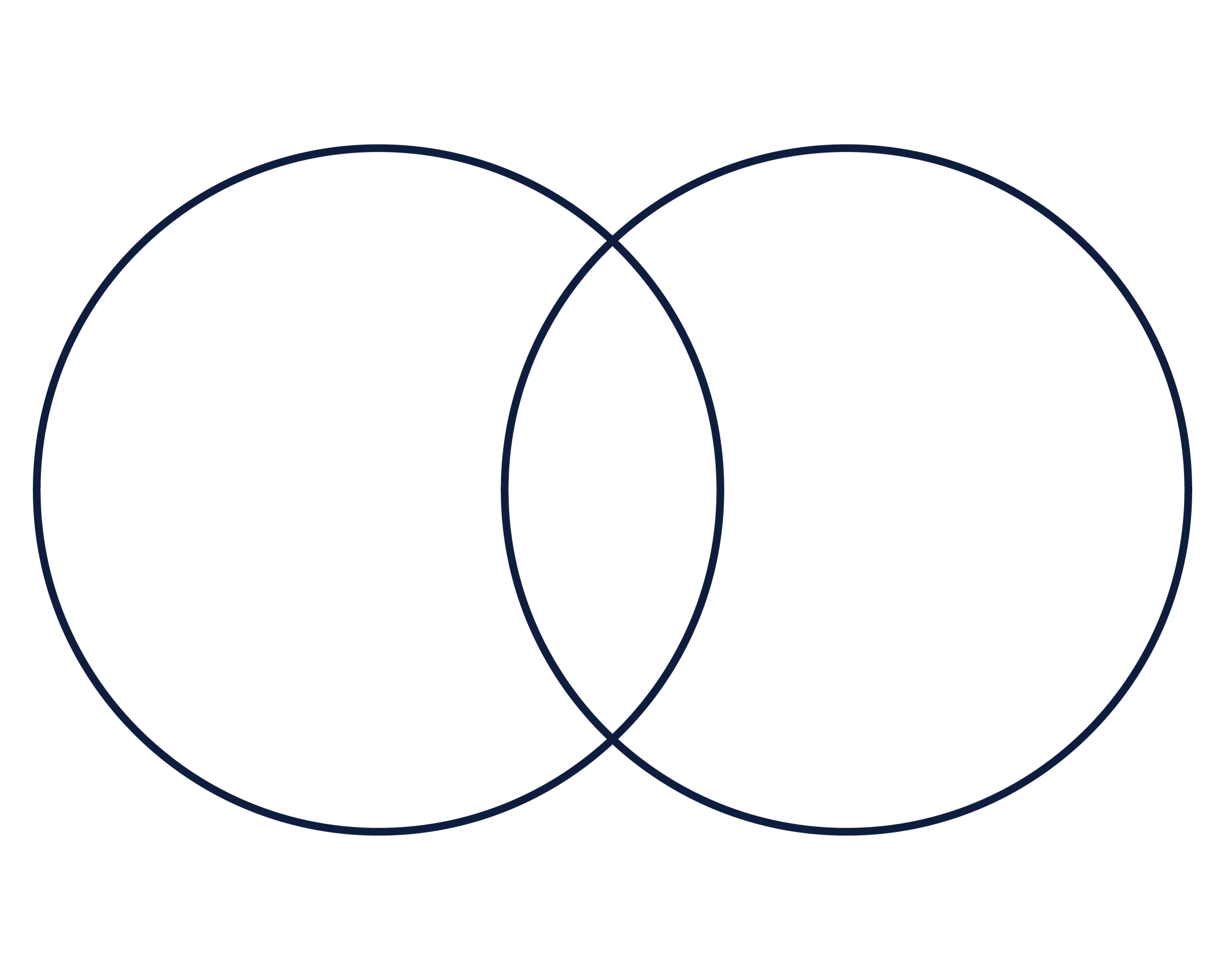
Venn diagram
Used to identify similarities and differences in multiple events.
Categorization
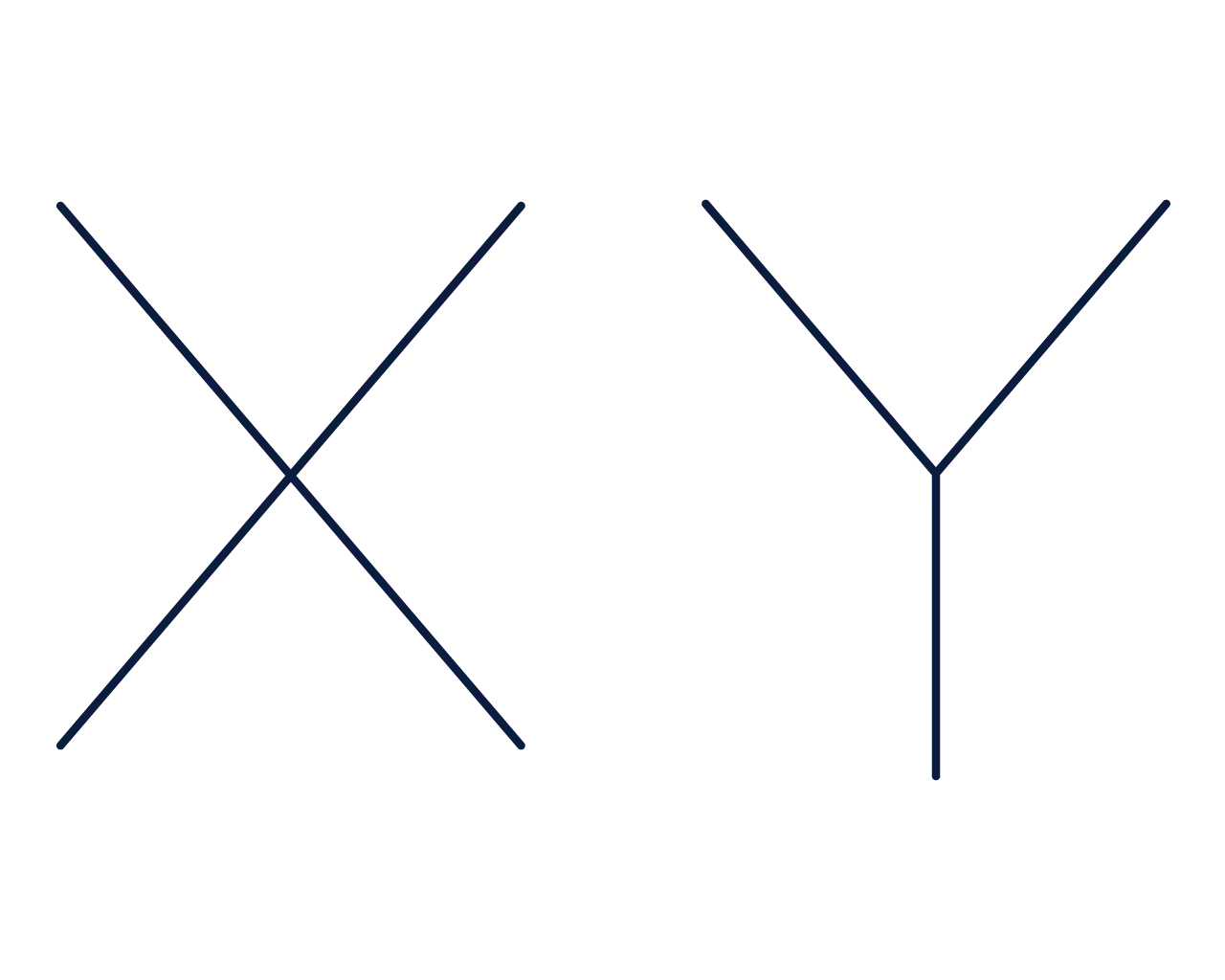
XY-chart
Used to categorize and organize things.
Correlation
Concept map
Used to find correlations between two subjects.
Broad-range analysis
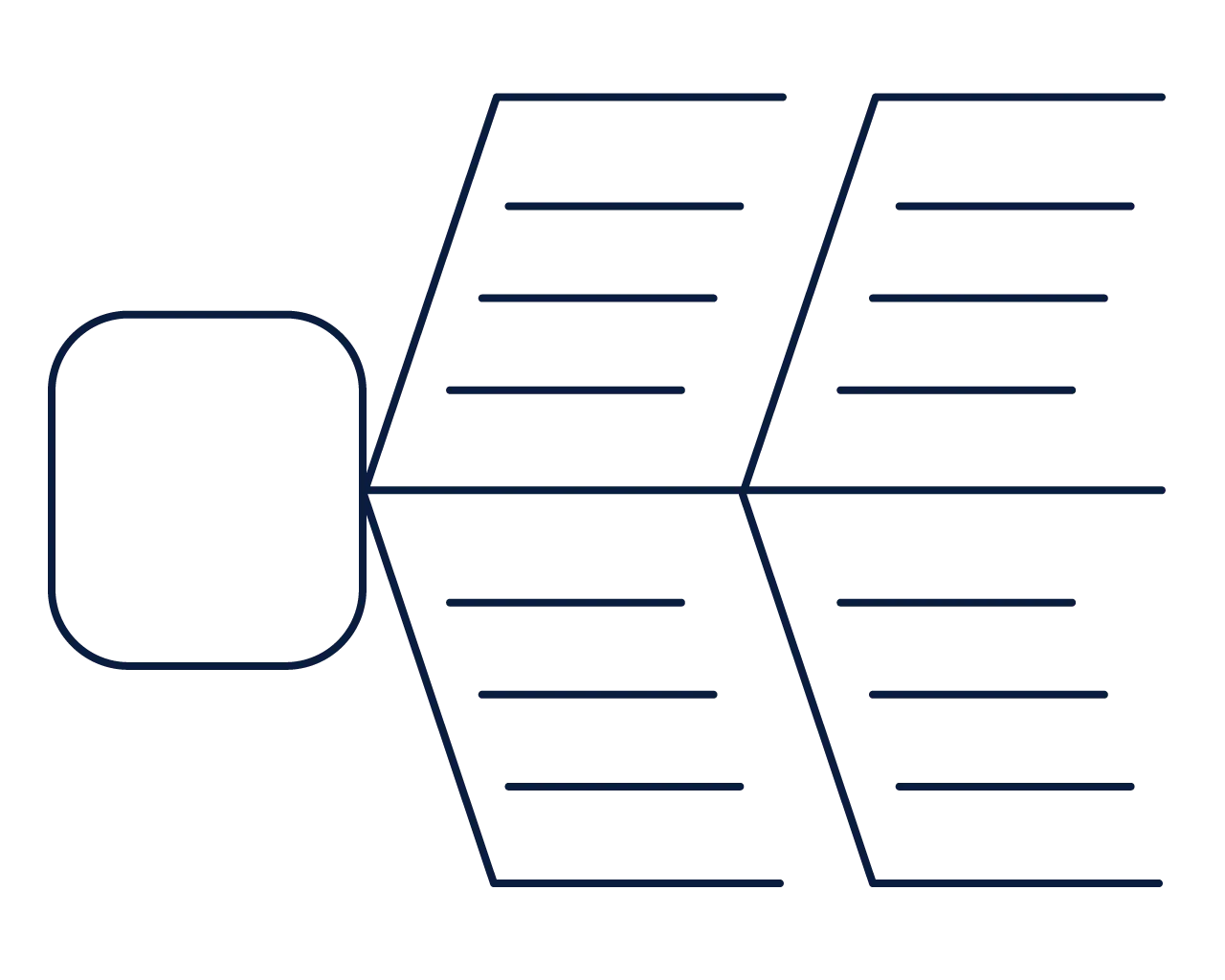
Fish bone chart
Used to organize information from multiple perspectives.
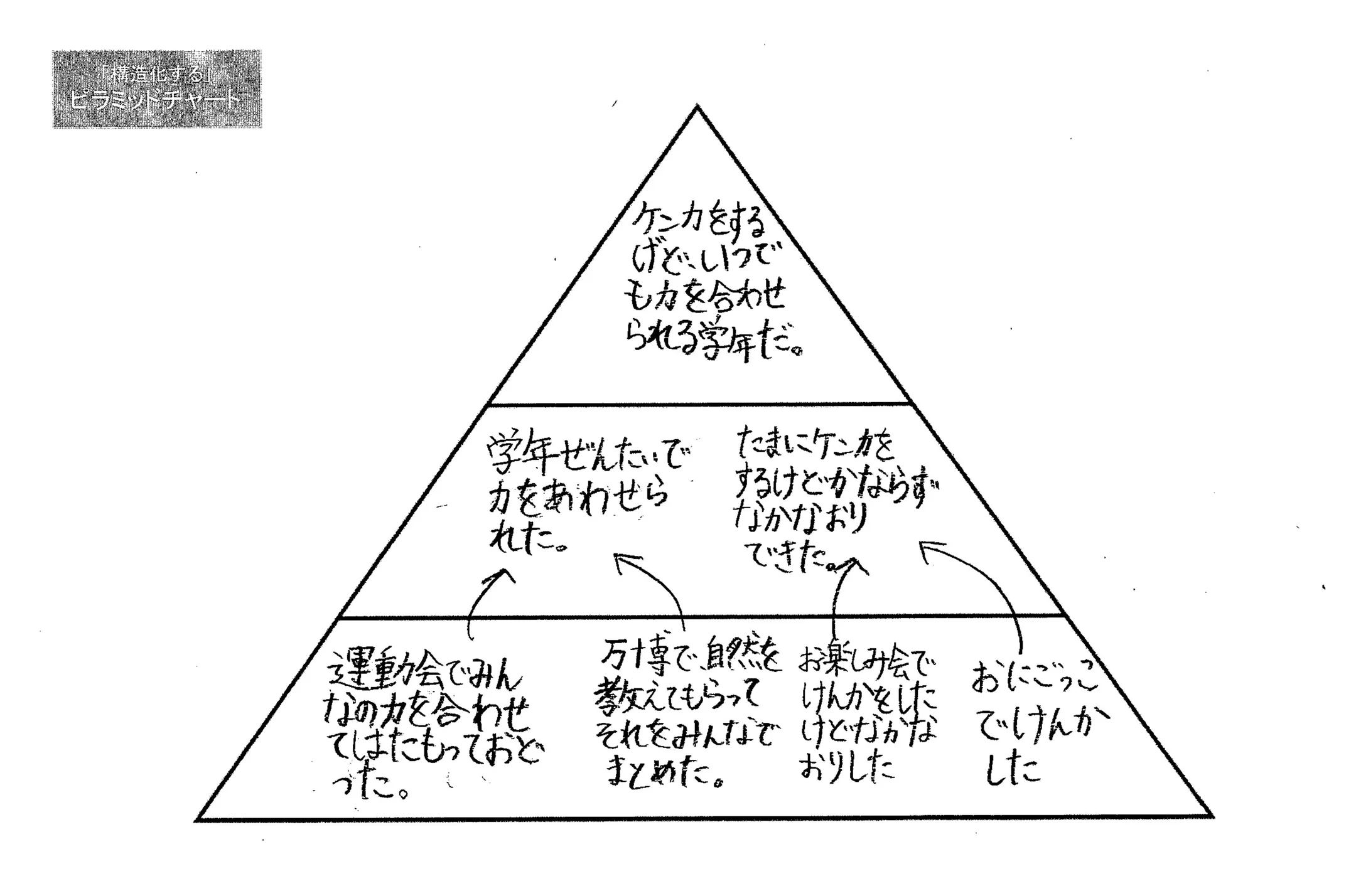
Construct
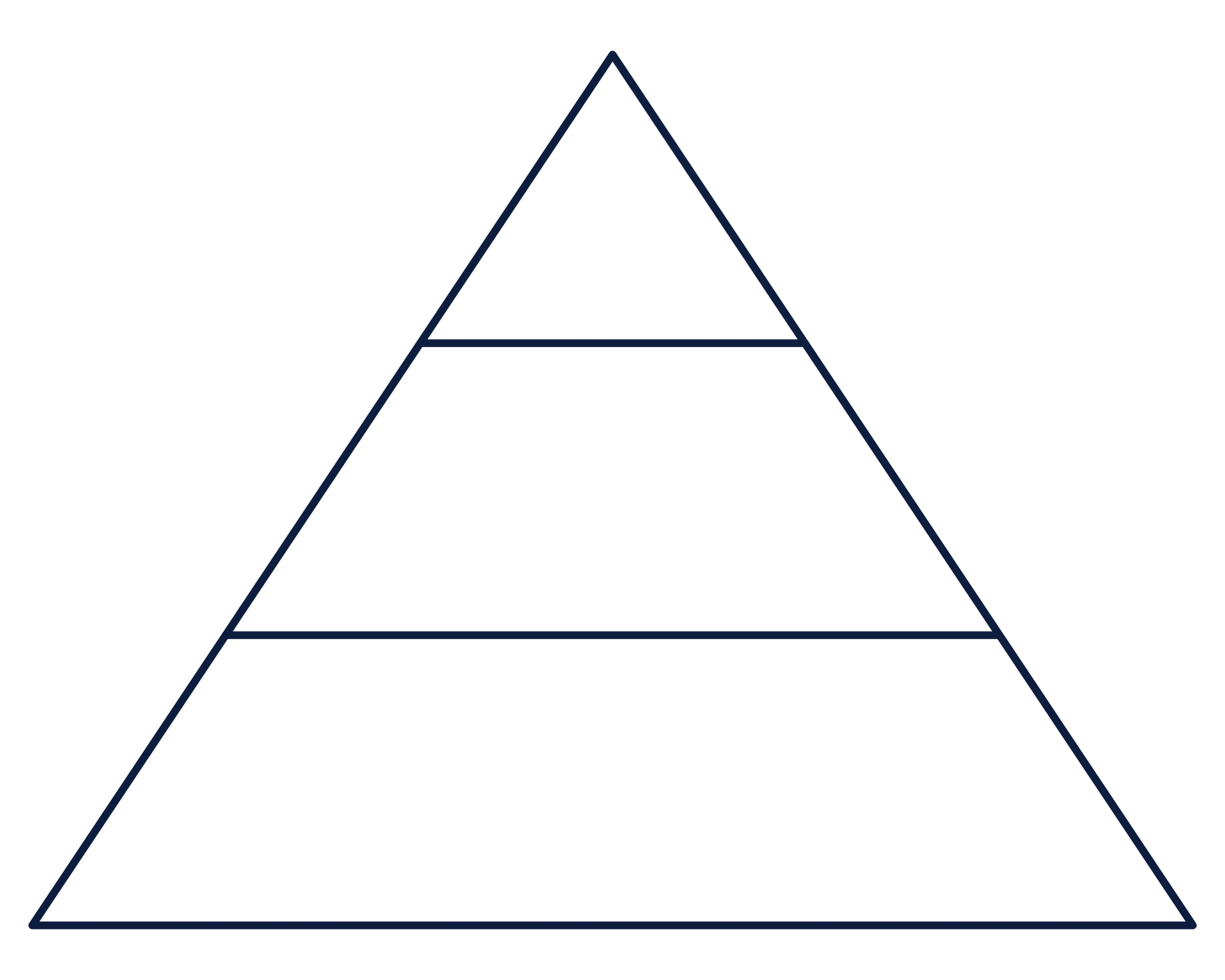
Pyramid graph
Used to logically frame an opinion based on evidence.
Expansion
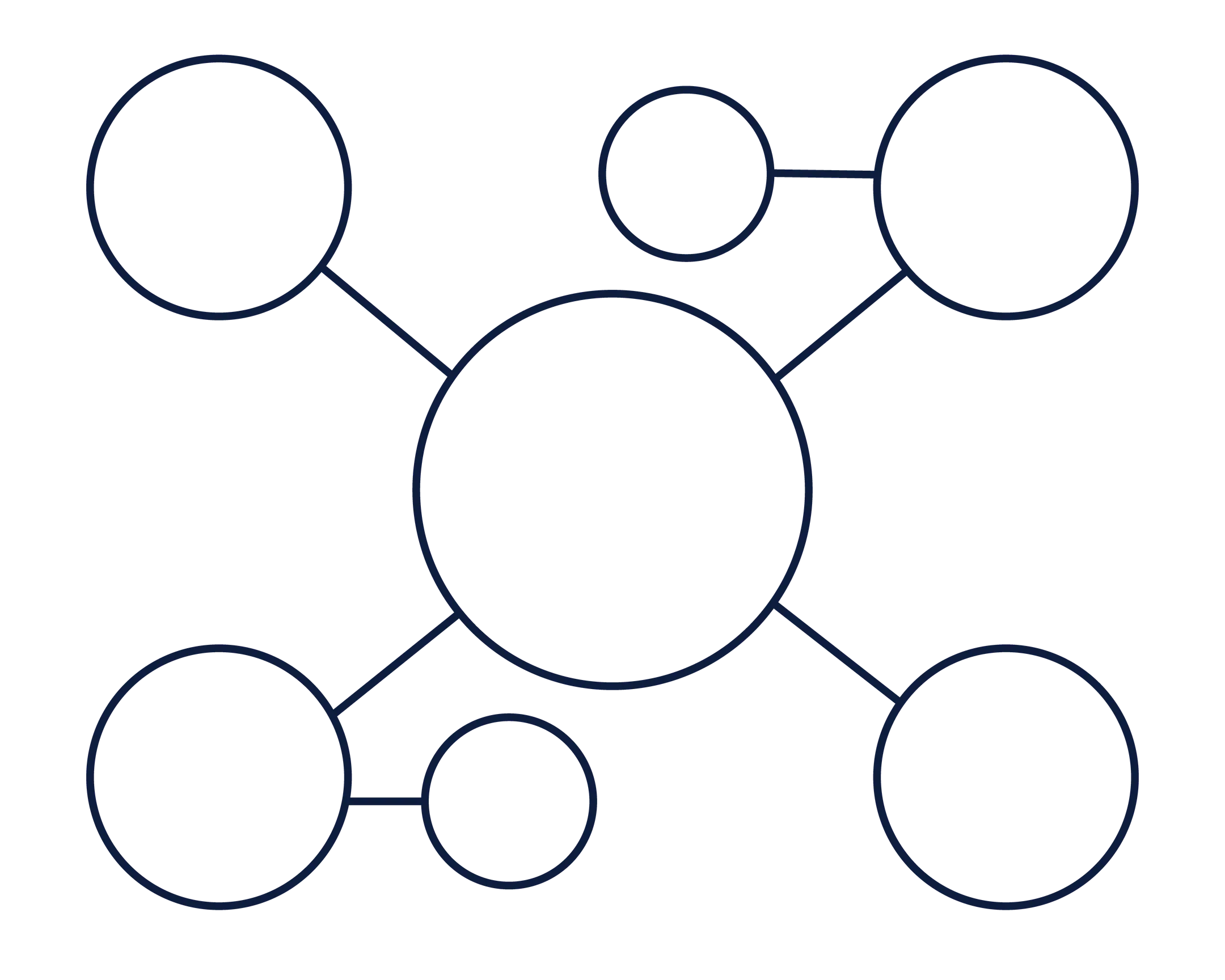
Image map
Used to expand imagination and creativity
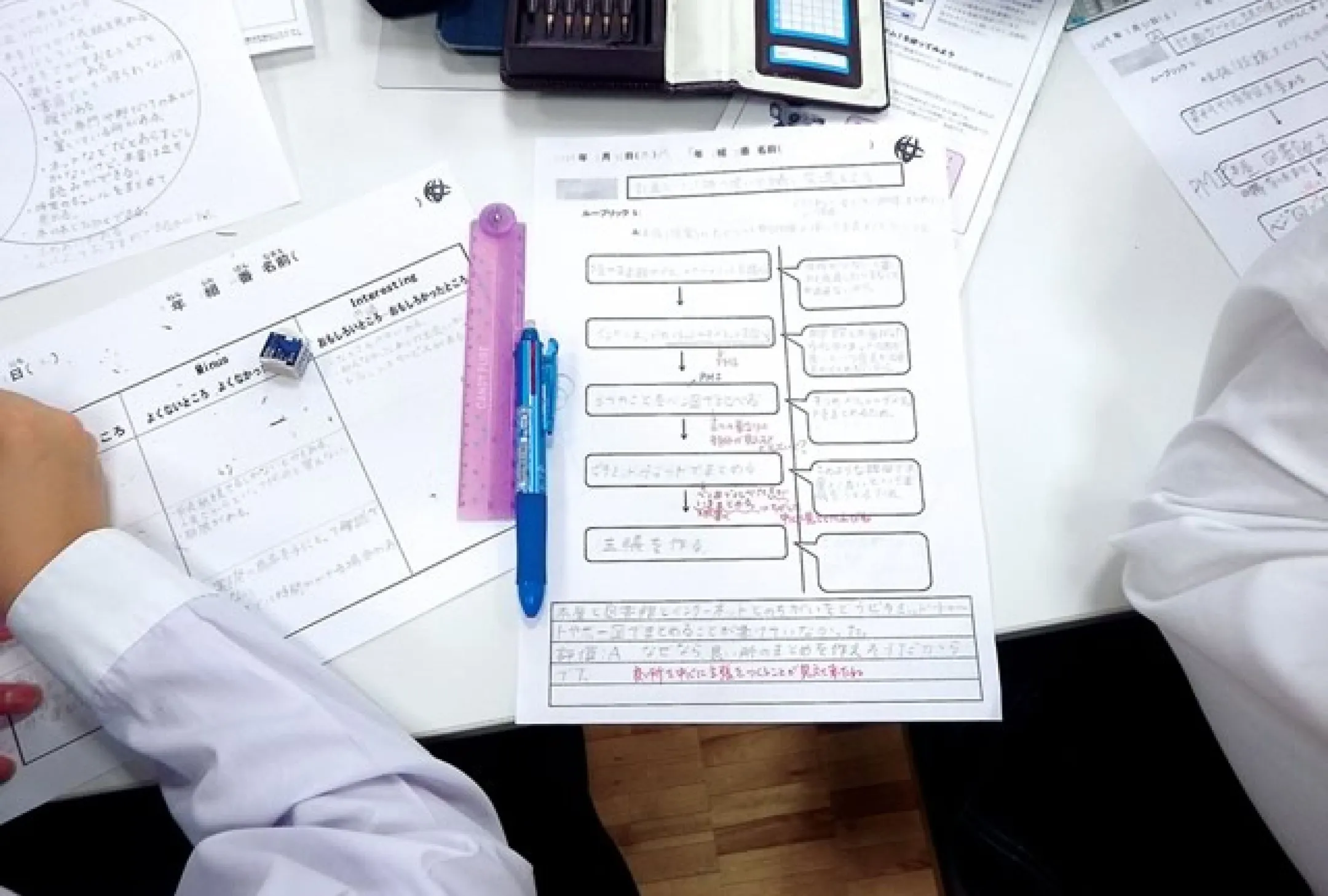
Working with teachers to set learning goals (Rubrics)
Children work with their teacher to set a learning goal to achieve in each lesson. As learning progresses, children tend to focus more on “research.” To prevent this, rubrics are used to redirect learning based on the previously-set goals and to promote learning with an emphasis on “how to think.” Students are encouraged to work toward their goals by sharing specific goals with their teachers.
Aiming to be an effective thinker

Developing thinking skills through repeated learning
Thinking skills cannot be acquired easily or quickly. It is important to repeatedly put into practice the thinking skills that are learned and to apply them to other subject areas. From this perspective, we have introduced various educational programs with an emphasis on the development of thinking power in many subject areas, in addition to the MUSE learning program. To ensure an integrated education that fosters logical thinking, we have designed special subjects to further develop our junior and senior high school students’ reasoning ability.
The Stage of Growth
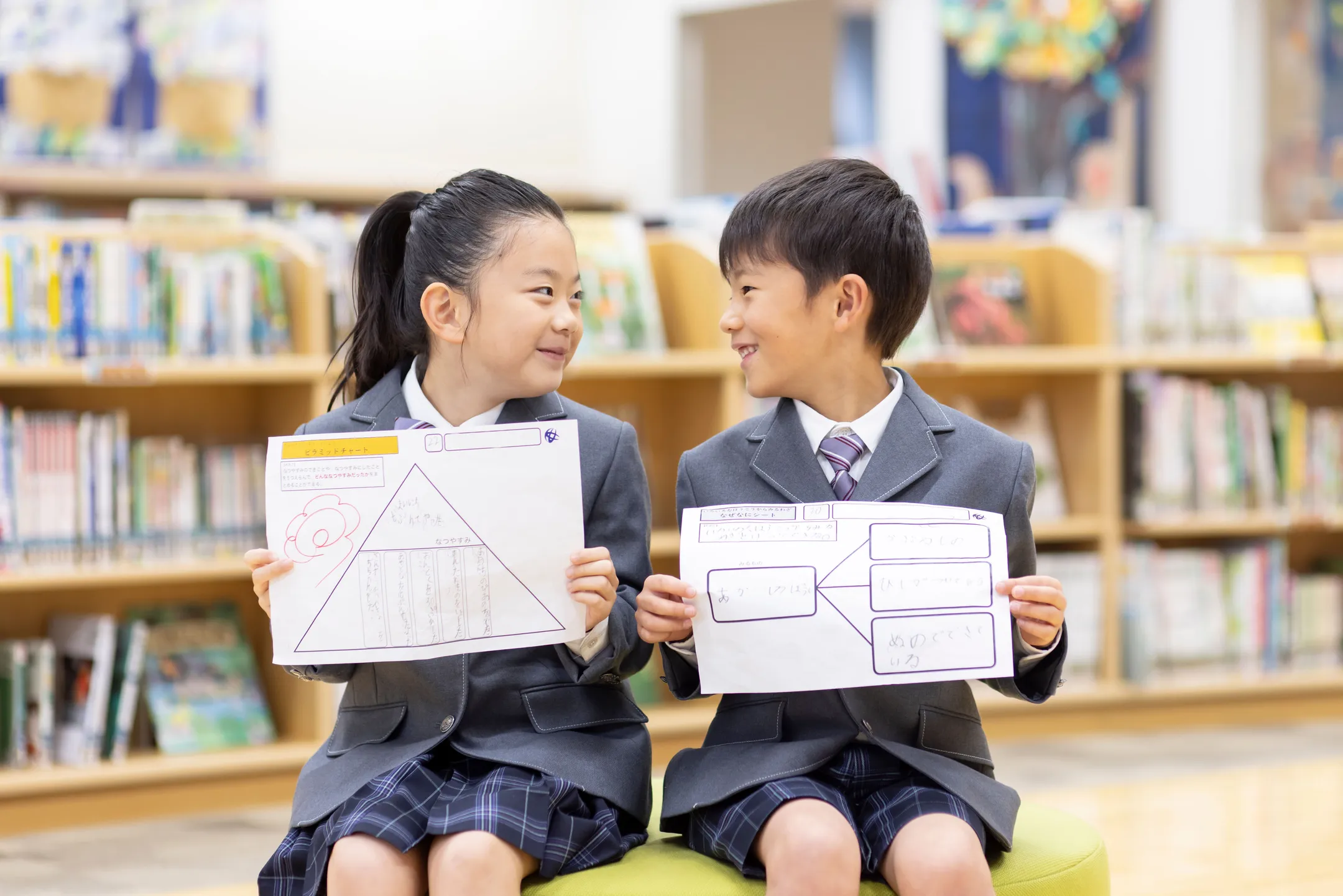
the first, second and third grades
Students in the first to third grades develop thinking skills by experiencing the joy of thinking directly, using six thinking tools.
Children working in a MUSE learning class
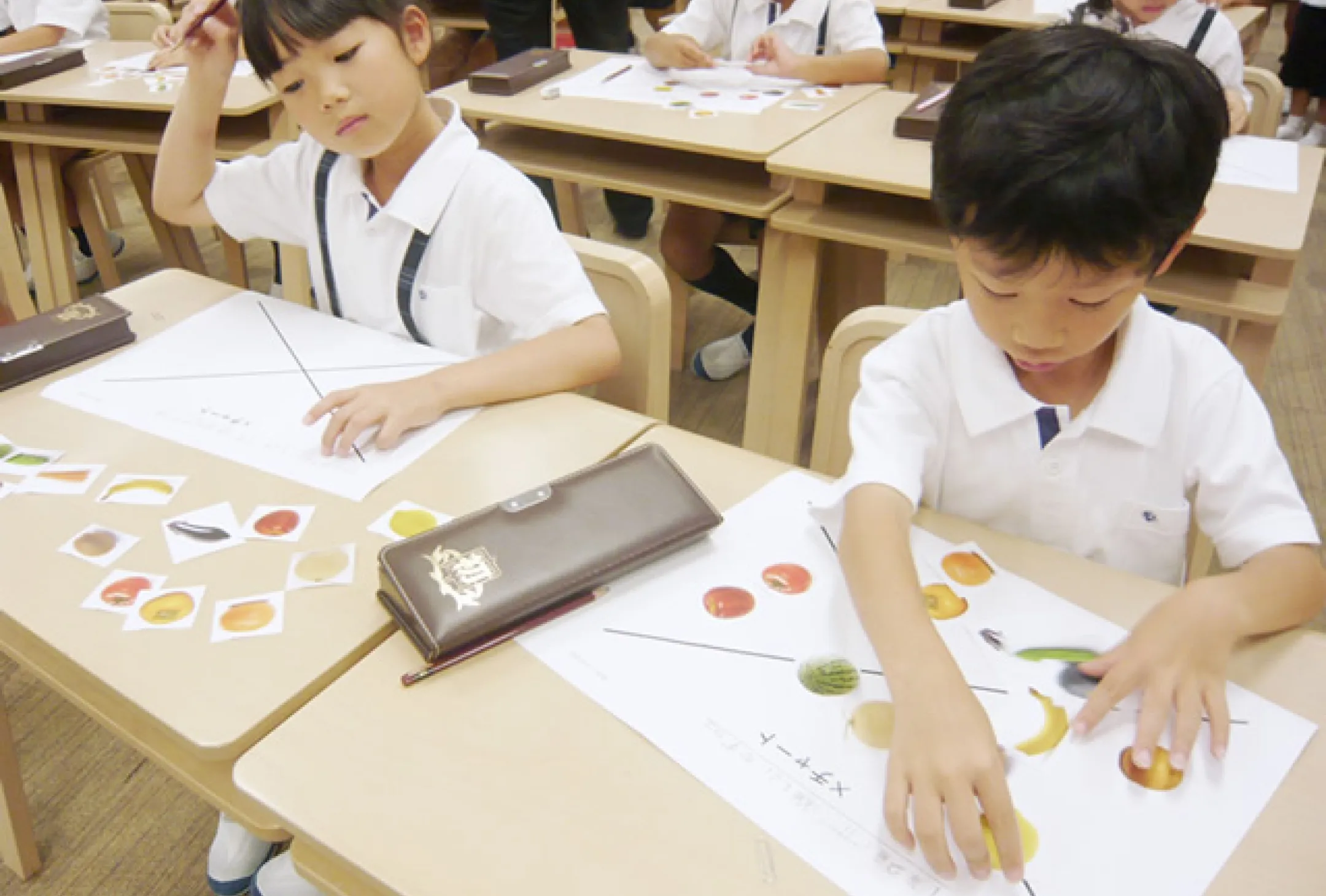
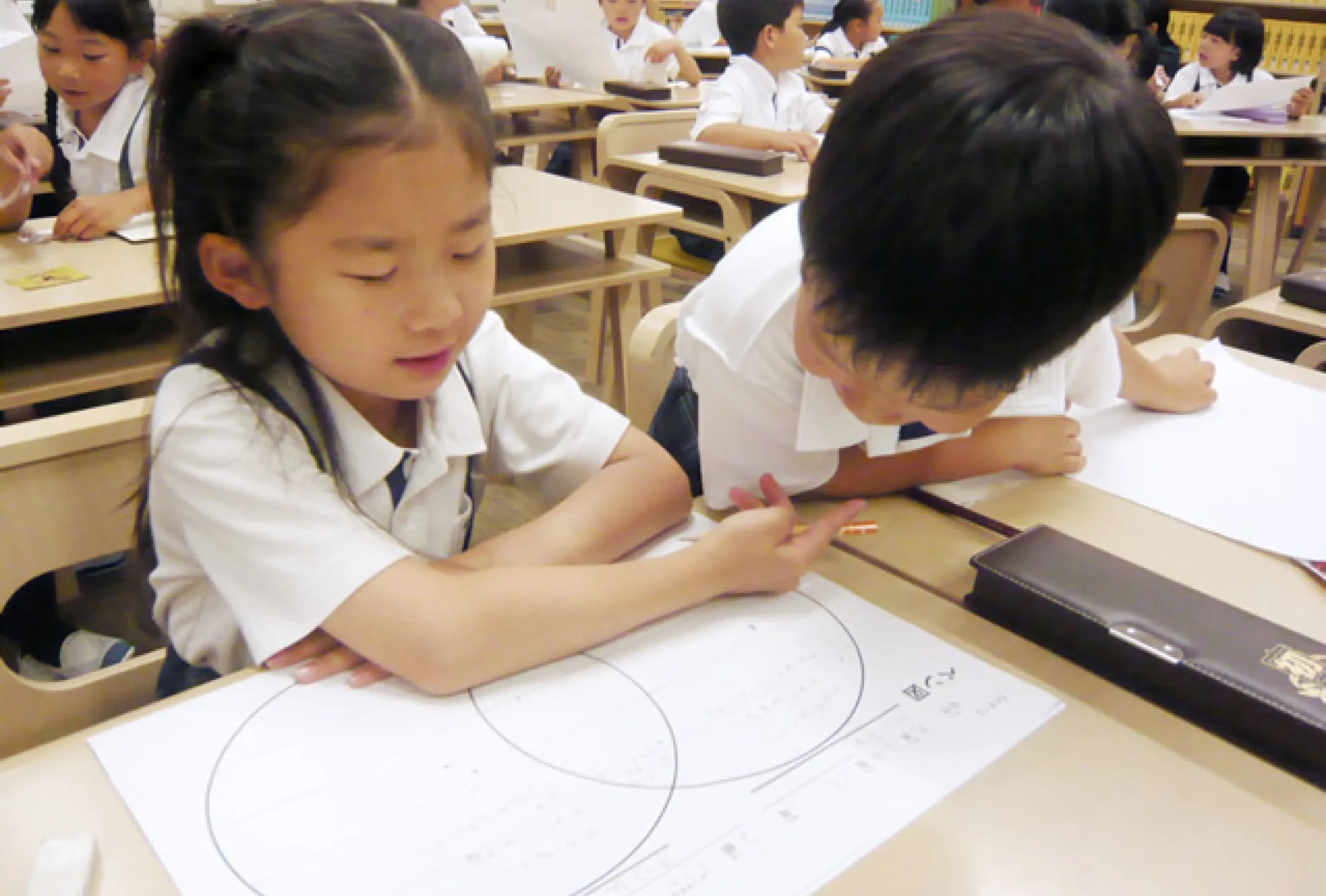


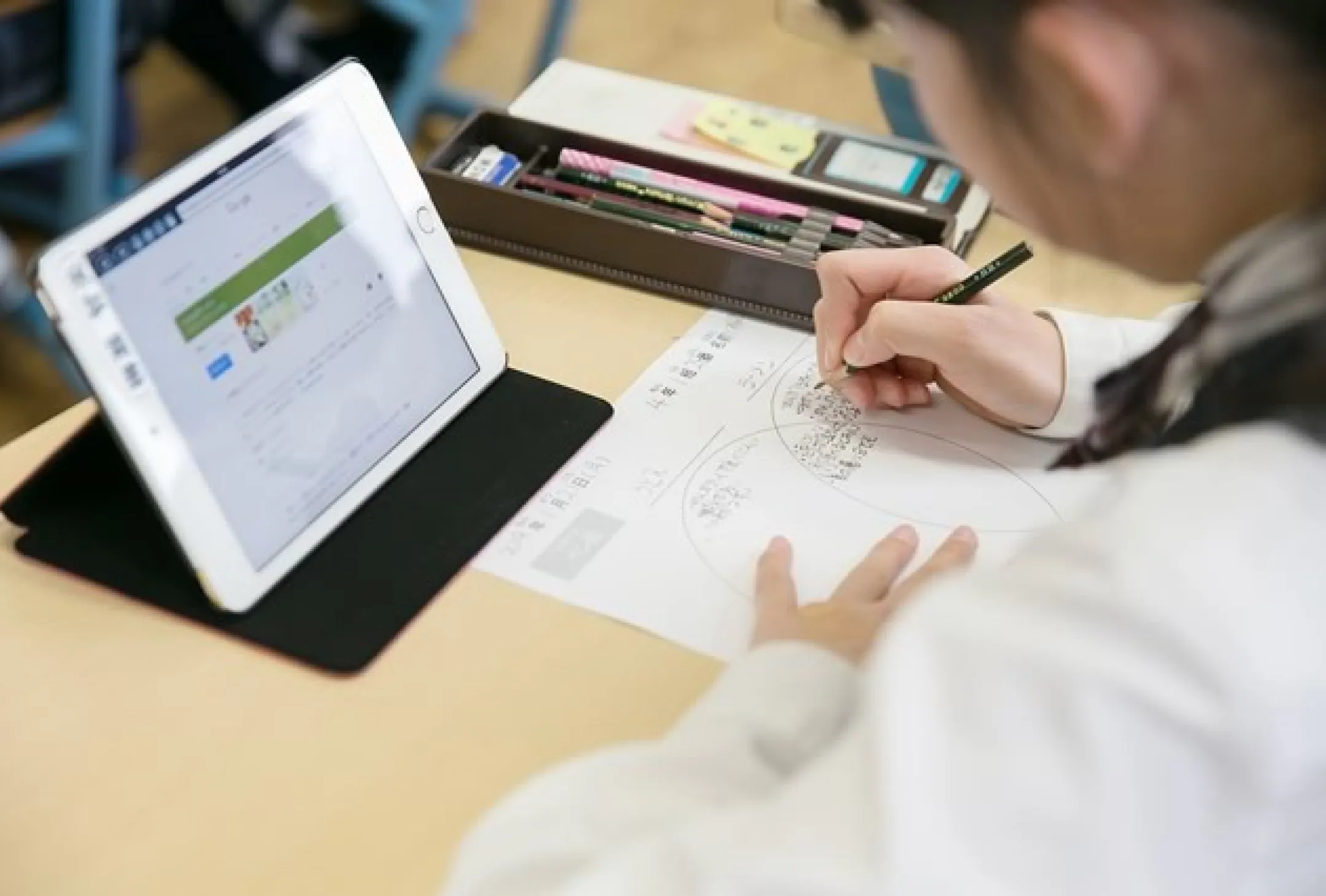
The Stage of Application
the fourth, fifth and six grades
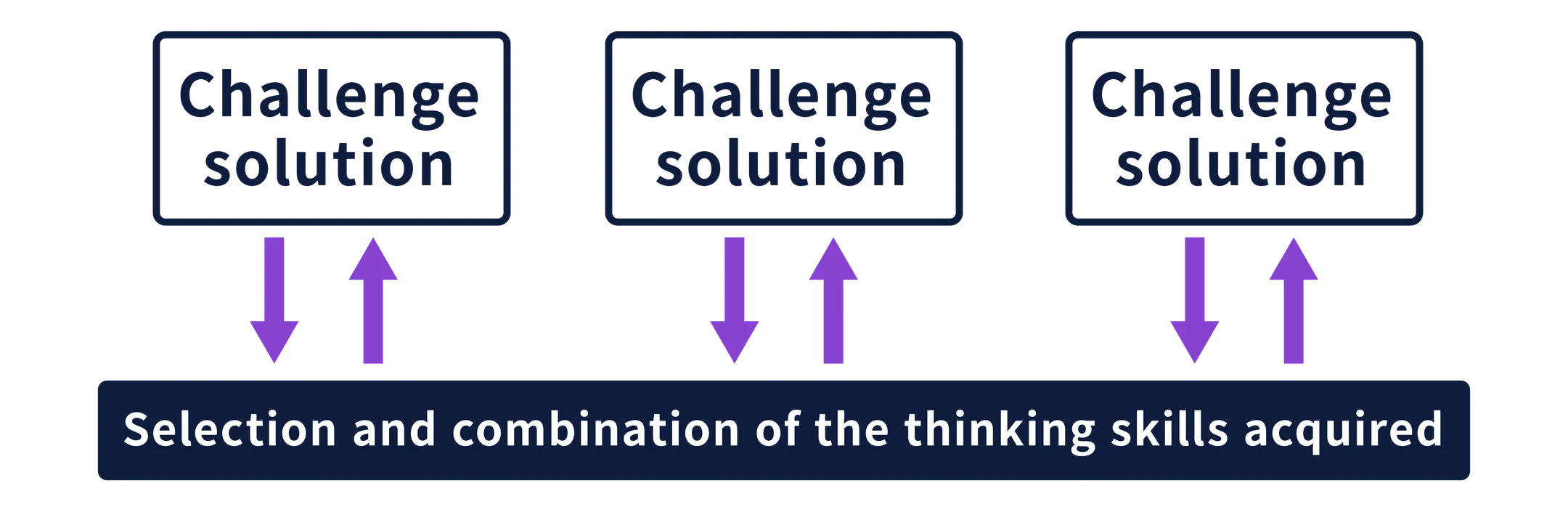
Children select thinking skills according to the type of problem and combine them to tackle their challenges.
Children working in a MUSE learning class
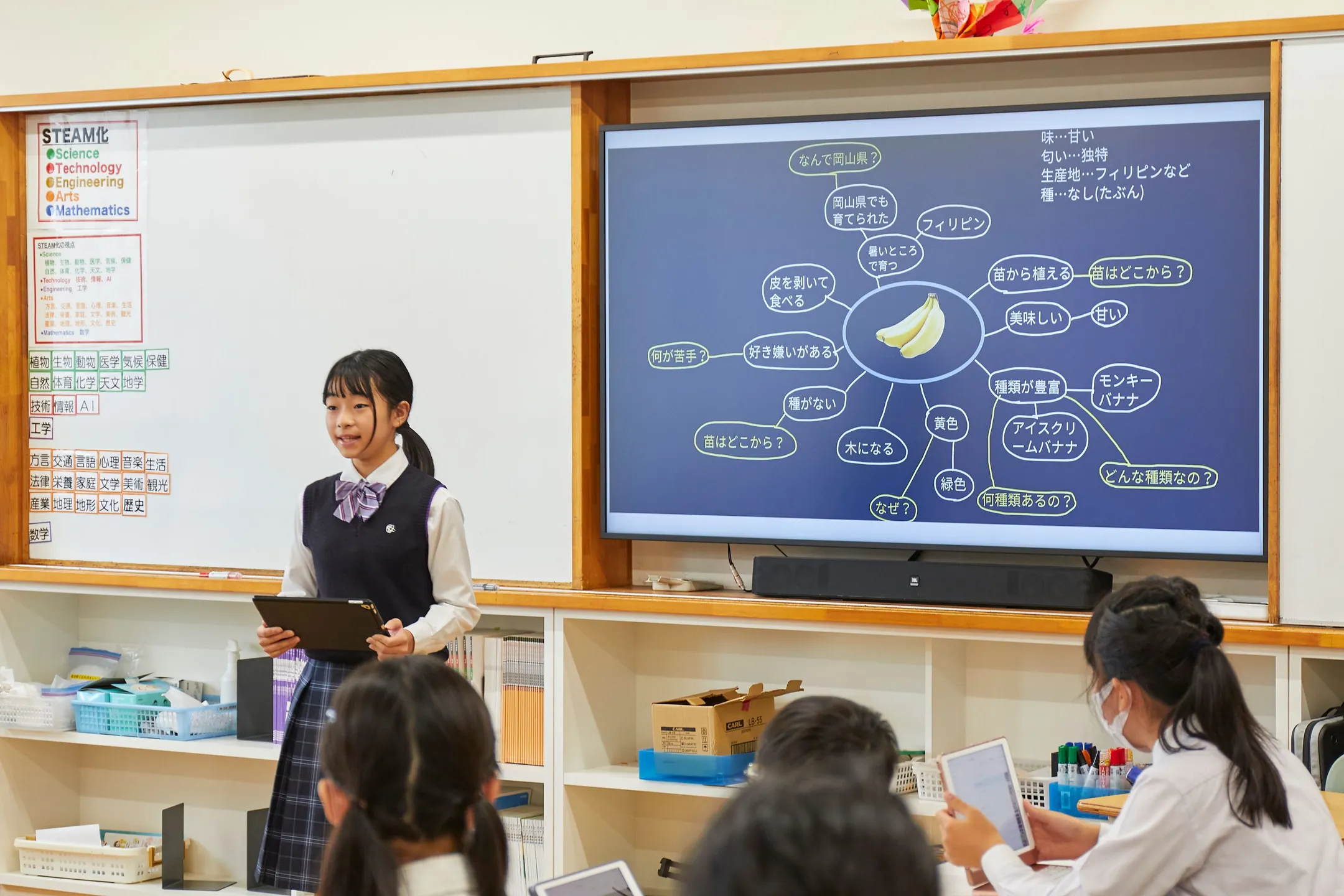


the fifth and six grades
Fifth and six graders are challenged to select necessary thinking skills according to their aim.

Children working in a MUSE learning class