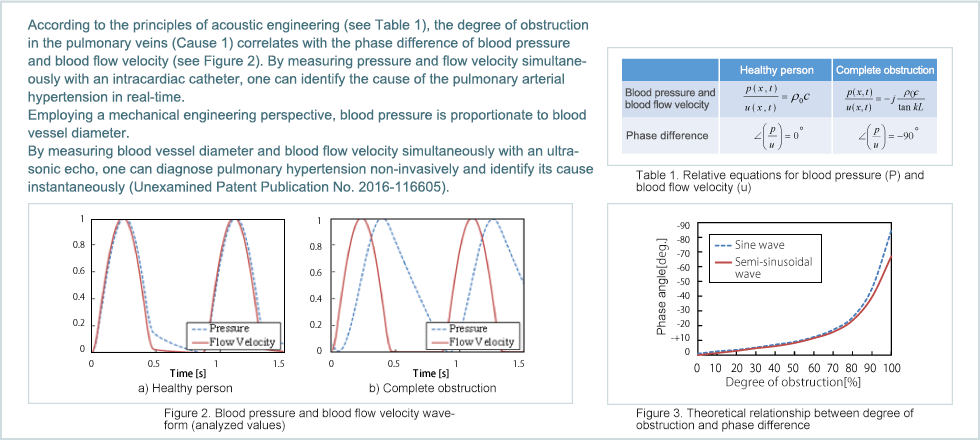
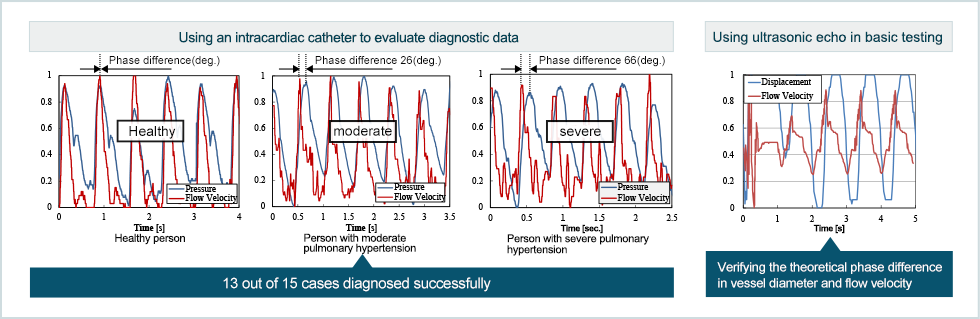
Pulmonary hypertension is a condition in which increased blood pressure in the arteries that send blood to the lungs, places a greater burden on the right ventricle and leads to a decline in blood circulatory function throughout the body.
It occurs in approximately 0.3% of newborn babies (around one million a year), and an increasing number of adults are contracting the condition. In Japan,the government has designated the condition as an intractable disease.
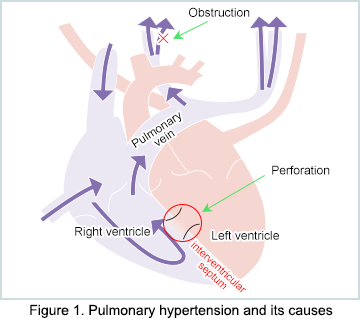
As shown in Figure 1, there are two known causes of pulmonary hypertension: (1) an obstruction in one of the arteries of the lung, and (2) perforation in the interatrial septum or interventricular septum. The treatment will vary depending on the cause, thus making it essential to identify the cause at the time of diagnosis.
The present approach for pulmonary hypertension is as follows: after the patient is screened using an echocardiogram or similar device, the pulmonary arterial blood pressure is measured more precisely using an intracardiac catheter, and the oxygen saturation in arterial blood samples is measured to identify the cause.