- Faculty Overview
- About Faculty of Societal Safety Sciences (FSS)
- Philosophy and Purpose of Establishment
- Curriculum
- Curriculum (For those enrolled before AY 2013)
- Message from the Dean
Curriculum
Concept of Curriculum Formation
The Faculty of Society Safety Sciences develops social-contribution-type human resources capable of practicing disaster mitigation, disaster prevention measures, accident prevention, risk management, and policy planning. In order to build a society where people can live safely and securely, students will acquire expertise on natural disasters and social disasters and think about which social systems should be constructed under what kind of institutions and policies.
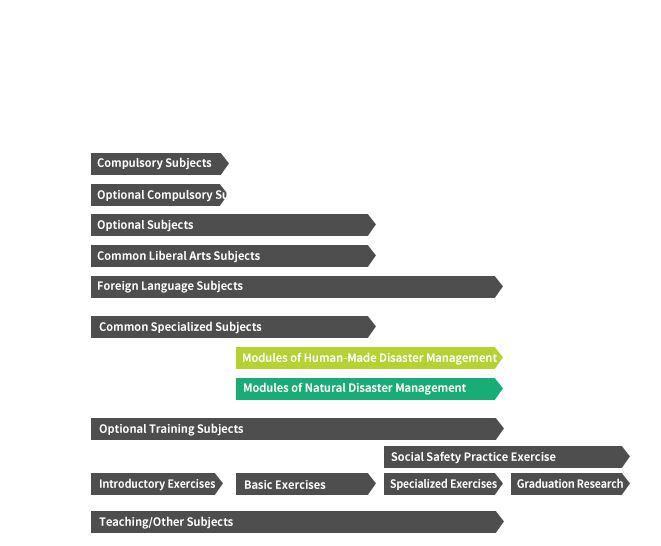
With the Faculty, students will focus on common and specialized basic education in the first year, specialized basic education and specialized intermediate education in the second year, and specialized advanced education and practical exercises in the third and fourth years. Course subjects are composed of four subject groups: basic subject group, specialized subject group, comprehensive subject group, and free subject group. The specialized subject group is further subdivided into three categories: common specialized subjects, social disaster management subjects, and natural disaster management subjects. The number of credits required for graduation is 124.
-
Modules of Human-Made Disaster Management
Students focus on various accidents and incidents that occur in modern industrial society and will learn accident prevention, disaster mitigation, occupational safety, human error, risk management, crisis management, corporate social responsibility (CSR), and safety institutional systems. The Faculty will cultivate human resources who can be active in companies and communities in order to realize a safer and more secure society.
-
Modules of Natural Disaster Management
The Faculty will develop human resources who can contribute to communities as disaster prevention and mitigation specialists. Students will acquire knowledge by analyzing the mechanisms of natural disasters. They will deepen their understanding of disaster prevention and mitigation methods, support for victims, recovery and reconstruction planning, the ideal state of self-help, mutual assistance, and public aids (administrative roles and self-responsibilities and public policies), and crisis management system.
Features of Curriculum Formation
The Faculty aims not only to enable students to learn theories and tools, but also to develop human resources capable of policy-making and practicing policies for disaster prevention and mitigation and accident prevention, crisis management by using the acquired theories and tools.
For the above purpose, the Faculty will teach the latest expertise in the academic discipline of social safety, and also conduct more practical education by incorporating simulation and hands-on training. The characteristics of the educational curriculum of the Faculty are summarized in the following four points:

- 01
- Students will systematically acquire the latest expertise on disaster prevention and mitigation, accident prevention, and crisis management.
- 02
- Students will learn practical skills through experiential learning and practical training.
- 03
- Students will learn skills, including social research, debate, presentation, advanced information processing, and English proficiency.
- 04
- Students will learn the ability to comprehensively understand the current situation of natural disasters and accidents and to formulate policies.
Through the curriculum consisting of the four subject groups of the aforementioned basic subject group, special subject group, integrated subject group, and free subject group, students make step-by-step progress from their first year until graduation.
Curriculum
Students will learn about fields related to disaster prevention and mitigation, accident prevention, and crisis management in an interdisciplinary and comprehensive manner, from the aspects of natural science, humanities, and social sciences. The curriculum aims to enhance students' ability to contribute to the realization of a safe and secure society by teaching and developing them. While students conduct education and research on social safety in general, they will acquire basic knowledge and methods, especially related to natural disasters, such as earthquakes and floods, and social disasters, centering on accidents. Furthermore, students will learn to improve their English communication skills.
- Basic Subjects
-
First
YearSecond
YearThird
YearFourth
YearCompulsory Subjects ■Introduction to Safety Science I ■Introduction to Safety Science II ■Practicum in Information Technology Optional Compulsory Subjects ■Mathematics I for Safety Science ■Mathematics II for Safety Science ■Statistics for Safety Science Optional Subjects ■Legal Systems for Safety in Society ■History of Technology and Society ■Contemporary International Society ■Theory of Legal Systems ■Public Administration ■Introduction to Economics ■Introduction to Business Management ■Modern History ■Contemporary History ■World Geography ■Philosophy ■Introduction to Logic ■Ethics ■Psychology ■Social Psychology ■Introduction to Physical Science ■Introduction to Geophysical Science ■Special Topic ■Endowed Chair Common Liberal Arts Subjects ■Health-Sports Science Activity a ■Health-Sports Science Activity b ■Health-Sports Science Activity c ■Study of Health-Sports Science ■Career Development for University Students ■Introductory Seminar in Career Development ■Career Development to Survive in Modern Society ■Introduction to SDGs ■Practice of SDGs ■The Origin of Environmental Problems and Policies ■Introduction to Carbon Neutrality ■AI and Data Science - Current Topics - ■AI and Data Science - Experiences - ■Introduction to Entrepreneurship to acquire Ability to Think and Act ■Entrepreneurship Practice to acquire Ability to Think and Act ■Practical Foundation of Data Science for Society ■Practice of AI and Data Engineering - Basic - ■Constitution of Japan ■Takatsuki City and Kansai University ■〔Challenge Subjects〕Each theme Foreign Language Subjects ■English I a ■English I b ■English II a ■English II b ■Practical English I a ■German I a ■German I b ■German II a ■German II b ■French I a ■French I b ■French II a ■French II b ■Russian I a ■Russian I b ■Russian II a ■Russian II b ■Spanish I a ■Spanish I b ■Spanish II a ■Spanish II b ■Chinese I a ■Chinese I b ■Chinese II a ■Chinese II b ■Korean I a ■Korean I b ■Korean II a ■Korean II b ■English III a ■English III b ■English IV a ■English IV b ■Practical English Ib ■Practical English II a ■Practical English II b ■Official-Test Accreditation 1 ■Official-Test Accreditation 2 ■Official-Test Accreditation 3 Green Letters: Compulsory Subjects
- Specialized Subject Group
-
First
YearSecond
YearThird
YearFourth
YearCommon Specialized Subjects ■Natural Disaster Case Studies ■Chemical and Environmental Risk ■Product Safety ■Introduction to Safety Systems ■History of Structures in Urban Areas ■Disaster Mitigation and Safety Education ■Introduction to Social Research ■Idee of ANZEN (=Japanese Notion of Safety) ■Administrative Law for Safety and Security ■Local Government Law ■Science and Technology for Society ■Public security policy ■Regulatory Compliance ■Public Policy ■Administration of Disaster Mitigation ■Business Law for Safely and Security ■Crisis Management ■Local Finance Law ■Economics of Risk and Disasters ■Transportation Safety ■Insurance ■Property and Casualty Insurance for Transport Safety ■Risk Management ■Crisis Management and Leadership ■Sociology of Risk and Disasters ■Risk Perception ■Risk Communication ■Research Methods for Behavioral Sciences ■Risk Assessment Methods ■Climate change and risks of global warming ■Applied Data Science ■Information Security ■Public Health Policy ■Business Continuity Planning ■Methods of Social Research ■Disaster Journalism Social Disaster Management Subjects ■Consumer Safety Law ■Criminology ■Disaster Psychology ■Human Errors ■Mental Health ■Crowd Safety ■Food Safety ■Safety of Medical Care and Pharmaceticals ■Accident Investigation ■Plant Design and Operation Safety ■Laborers Safety and Health ■Infectious Disease Control and Management Natural Disaster Management Subjects ■Urban Design for Disaster Mitigation ■Earthquake Disaster ■Chemical Substances and Environmental Risk ■Hydrosphere Disaster ■Geodisaster ■Seismic Engineering ■Integrated Disaster Reduction ■Disaster Response and Recovery ■Fire Disaster ■Environmental Policy ■Disaster Information Green Letters: Compulsory Subjects
- Integrated Subject Group
-
First
YearSecond
YearThird
YearFourth
YearElective Practice Subjects ■Practicum in Mathematics ■Practicum in Artificial Intelligence ■Practicum in Social Safety ■Practicum in Statistical Analysis I ■Practicum in Statistical Analysis II ■Practicum in Geographic Information System ■Practicum in Disaster Simulation ■Practicum in Disaster Survey ■Accident Investigation Seminar ■Practicum in Social Research I ■Practicum in Social Research II ■Practicum in Product Design ■Practicum in Behavioral Sciences Compulsory Training Subjects ■Introductory Seminar ■Basic Seminar ■Advanced Seminar I ■Advanced Seminar II ■Graduation Thesis I ■Graduation Thesis II Elective Training Subjects ■Practical exercise of Societal Safety Sciences Green Letters: Compulsory Subjects
- Foreign Student Course
-
First Year Second Year Third Year Fourth Year Compulsory Subjects ■Japanese I a ■Japanese I b ■Japanese II a ■Japanese II b ■Japanese III a ■Japanese III b ■Japanese IV a ■Japanese IV b ■Japanese V a ■Japanese V b ■Japanese VI a ■Japanese VI b Optional Subjects ■Contemporary Japan I ■Contemporary Japan II ■Practical Business Communication in Japanese I ■Practical Business Communication in Japanese II ■Career Design I (Japanese Society and Companies) ■Career Design II (Employment and Working Life in Japan) ■Career Design III (Working in Japanese Society) ■Contemporary Japan(Understanding Japan) ■Contemporary Japan(Researching Japan) ■Contemporary Japan(Japan in Mass Media 1) ■Contemporary Japan(Japan in Mass Media 2) ■Communication in Japanese Society(Learning Kansai 1) ■Communication in Japanese Society(Learning Kansai 2) ■Communication in Japanese Society(Business Japanese) ■Communication in Japanese Society(JPN Corporate Culture) ■Field-Based Learning(Society and Workplace Culture in Japan ■Japanese(1-a) ■Japanese(1-b) ■Japanese(2-a) ■Japanese(2-b) ■Japanese(3-a) ■Japanese(3-b) ■Japanese(4-a) ■Japanese(4-b) ■Japanese(5-a) ■Japanese(5-b) ■Japanese(6-a) ■Japanese(6-b) ■Japanese(7-a) ■Japanese(7-b)
- Free Subject Group
-
First
YearSecond
YearThird
YearFourth
Year■Introduction to the Teaching Profession ■Principles of Education ■Outline of Japanese History I ■Outline of Japanese History II ■Collection Development ■Oriental History ■Occidental History ■Regional Geography I ■Regional Geography II ■Outline of Geography I ■Outline of Geography II ■Educational Institution ■Human Rights Education ■Educational Psychology ■Methods of Teaching Social Sciences I ■Methods of Teaching Social Sciences II ■Methods of Teaching Civics I ■Methods of Teaching Civics II ■Theory and Method of Moral Education ■Extracurricular Activities ■Instructional Methods and Technology ■Educational Counseling ■Organization of Information and Knowledge ■School Management and Libraries ■School Libraries in Education ■Reading and Personality ■Practicum in Use of School Library Media ■Curriculum Development ■Methods of Teaching Social Sciences III ■Methods of Teaching Social Sciences IV ■Career Guidance for Students ■Pre-Guidance and Training for Teaching Practice ■Special Needs Education ■Teaching Methods of the Period for Integrated Studies ■Student Teaching Practice II ■Practice Seminar for Teaching Profession (Junior & Senior High School Education) ■Student Teaching Practice I ■Internship Green Letters: Compulsory Subjects